Conflict News: Breaking News on International Conflicts and Resolutions

The war in Ukraine continues to represent one of the most significant armed conflict in Europe since World War II, with global implications for security, economics, and humanitarian concerns.
Current Military Situation
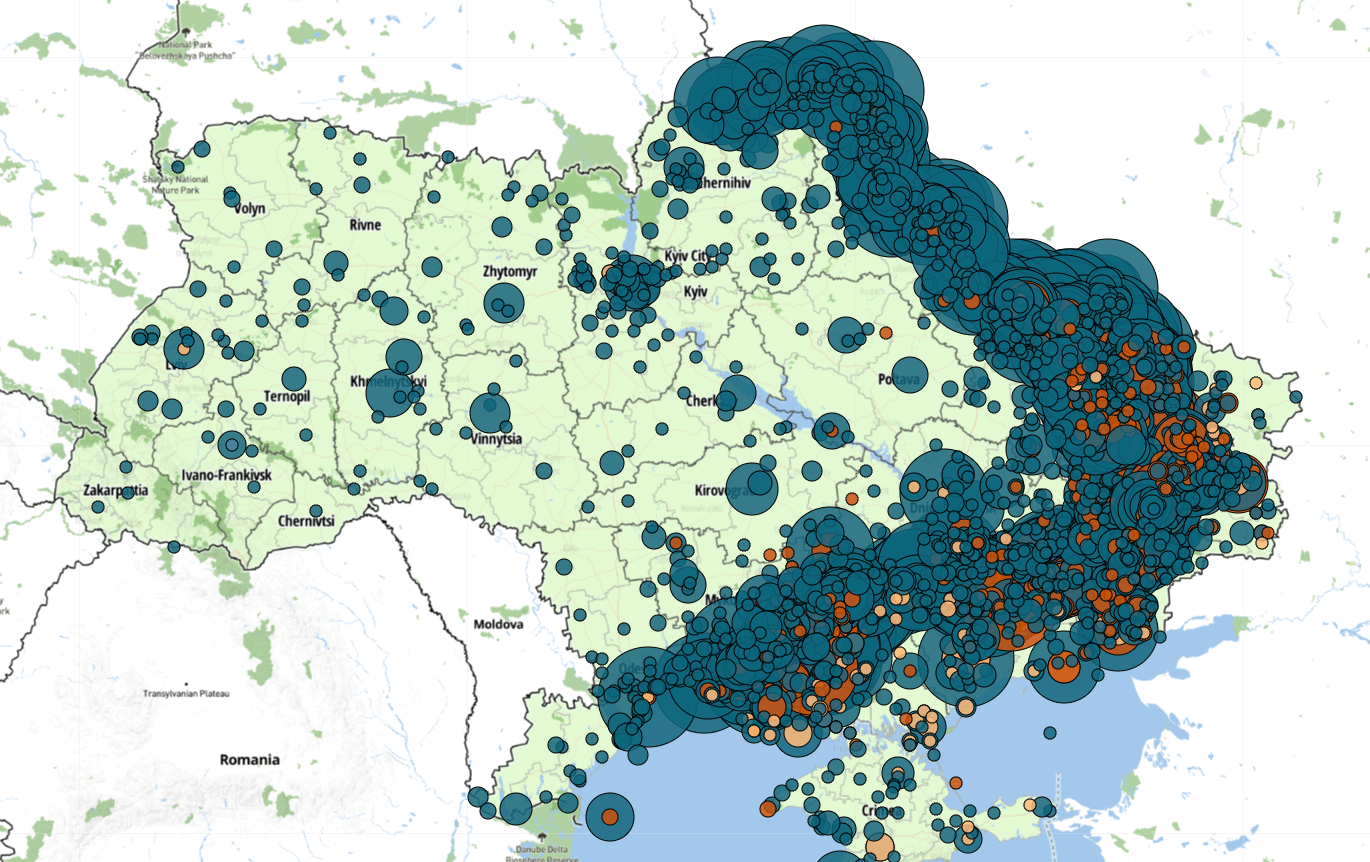
- Fighting remains concentrated in eastern Ukraine, particularly in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions
- Russian forces continue to hold approximately 18% of Ukrainian territory
- Ukrainian defensive positions face ongoing pressure along the eastern front
- Artillery and drone warfare dominate tactical operations on both sides
- Critical infrastructure including power plants and water facilities remain targets
Diplomatic Developments
- Peace proposal frameworks continue to circulate among international mediators
- Neutral nations have attempted to facilitate dialogue between the warring parties
- UN General Assembly resolutions continue to call for Russian withdrawal
- Regional security architectures are being reassessed in response to the ongoing conflict
Humanitarian Impact
- Civilian casualties continue to mount with estimates exceeding 10,000 deaths
- Over 6 million Ukrainians remain externally displaced across Europe
- Critical utilities face disruption heading into colder weather
- Humanitarian corridors operate inconsistently, complicating aid delivery
- Ongoing concerns about nuclear safety at power plants in conflict zones
International Response
- Military aid packages continue from Western allies, though debates persist about scope and restrictions
- Economic sanctions on Russia remain in place with varying degrees of enforcement
- Energy dependencies across Europe continue to be restructured
- NATO expansion with Finland and Sweden changing regional security dynamics
Middle East Conflict
The situation in Gaza and the broader Middle East remains extremely volatile with profound humanitarian concerns.
Current Situation
- Fighting continues with significant civilian impact
- Humanitarian access remains severely restricted in many areas
- Regional concerns about conflict expansion persist
- Infrastructure damage has created critical shortages of basic necessities
Diplomatic Efforts
- Multiple ceasefire proposals have been presented by regional and international mediators
- Egypt, Qatar, and the United States remain central to negotiation efforts
- United Nations Security Council has held emergency sessions without reaching consensus on binding resolutions
- Regional diplomatic initiatives continue to seek de-escalation pathways
Humanitarian Crisis
- Acute shortages of food, medicine, clean water, and fuel
- Healthcare system operating under extreme duress with limited supplies
- Displacement of civilians creating overcrowded shelters
- International aid organizations face significant challenges in delivering assistance
Broader Regional Implications
- Tensions along the Israel-Lebanon border with Hezbollah exchanges
- Iranian positioning and proxy group activities across the region
- Red Sea shipping disruptions affecting global commerce
- Regional alliances being tested by the ongoing conflict
Sudan’s Civil War
What began as a power struggle between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) has evolved into a full-scale civil war with catastrophic humanitarian consequences.
Military Situation
- Fighting concentrated in Khartoum, Darfur, and Kordofan regions
- Control of territory remains fragmented and fluid
- Both sides accused of targeting civilian areas and infrastructure
- Increasing reports of ethnically-motivated violence, particularly in Darfur
Humanitarian Emergency
- The UN describes Sudan as facing “the world’s largest displacement crisis”
- Over 9 million people internally displaced
- Famine conditions emerging in conflict-affected areas
- Healthcare system collapse with 70-80% of hospitals in conflict zones non-functional
- Restricted humanitarian access preventing aid delivery
International Response
- IGAD (Intergovernmental Authority on Development) mediation efforts ongoing
- Saudi and US-brokered talks have failed to produce lasting ceasefires
- Limited international media attention despite scale of the crisis
- Humanitarian funding appeals significantly underfunded
- Concerns about regional destabilization with refugee flows to Chad, South Sudan, and Egypt
Myanmar’s Ongoing Crisis
Since the military coup in February 2021, Myanmar has experienced escalating conflict between the military junta and diverse resistance forces, including ethnic armed organizations and People’s Defense Forces.
Current Situation
- Fighting has intensified across multiple states, including Rakhine, Shan, and Kayah
- The National Unity Government (NUG) and allied resistance forces have made territorial gains
- Military junta faces increasing challenges maintaining control
- Civilian casualties mounting with airstrikes and artillery used in populated areas
Humanitarian Impact
- Over 2.6 million people internally displaced
- Systematic destruction of villages and civilian infrastructure
- Food insecurity affecting an estimated 17.6 million people
- Healthcare system collapsed in many areas
- Education disrupted for millions of children
International Dimensions
- ASEAN’s Five-Point Consensus largely ineffective in resolving the crisis
- China’s complex role as both economic partner and mediator with ethnic armed groups
- Limited Western leverage beyond sanctions
- Refugee flows affecting Thailand, India, and Bangladesh
Simmering Conflicts and Potential Flashpoints
Sahel Region Instability
The Sahel region of Africa continues to face overlapping security, governance, and humanitarian challenges.
Current Developments
- Military governments in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger coordinating regional security approaches
- French military withdrawal and Russian Wagner Group presence changing security dynamics
- Jihadist groups including JNIM and ISGS expanding territorial control in rural areas
- Civilian casualties increasing with allegations of abuses by all armed actors
Humanitarian Concerns
- Over 4.8 million people displaced across the Central Sahel
- Food insecurity affecting nearly 20 million people
- Climate change exacerbating resource competition and displacement
- Closure of schools affecting millions of children
International Engagement
- UN peacekeeping mission (MINUSMA) withdrawal from Mali completed by December 2023
- ECOWAS sanctions and diplomacy with military governments showing limited results
- Competing international influences between Western powers, Russia, and China
- Concerns about fragmentation of regional security architecture
Taiwan Strait Tensions
Cross-strait relations between China and Taiwan remain a potential flashpoint with global implications.
Recent Developments
- Increased Chinese military exercises around Taiwan, including encirclement drills
- Ongoing diplomatic isolation efforts targeting Taiwan’s international recognition
- Taiwan’s defense modernization and military preparedness enhancements
- U.S. arms sales and unofficial diplomatic engagement with Taiwan
Strategic Implications
- Global semiconductor supply chain vulnerabilities highlighted by potential conflict
- Major shipping routes potentially threatened by any escalation
- Regional alliance systems being tested by tensions
- Risk calculations constantly evolving among all stakeholders
Diplomatic Positioning
- “One China” policy interpretations continuing to evolve
- Taiwan’s international participation in organizations like WHO remaining contested
- Regional security dialogues increasingly focused on Taiwan contingencies
- Economic interdependence creating complex risk calculations
Horn of Africa Security Dynamics
The Horn of Africa faces multiple interconnected conflicts and security challenges.
Ethiopia’s Fragile Peace
- Tigray conflict officially ended by peace agreement but implementation challenges remain
- New conflicts emerging in Amhara and Oromia regions
- Humanitarian recovery slow with ongoing food insecurity
- Regional tensions with Somalia and disputes over resources
Somalia’s Struggle Against Al-Shabaab
- Offensive operations against Al-Shabaab showing mixed results
- ATMIS (African Union Transition Mission in Somalia) transitioning responsibilities
- Political tensions between federal government and member states
- Climate crises exacerbating displacement and food insecurity
Resolution Mechanisms and Peace Processes
United Nations Peacekeeping Operations
The UN currently deploys approximately 87,000 personnel across 12 peacekeeping missions globally.
Key Operations:
- MONUSCO (Democratic Republic of Congo): Phased withdrawal underway amid criticisms of effectiveness
- UNMISS (South Sudan): Protection of civilians remains primary focus as peace process stalls
- MINUSMA (Mali): Completed withdrawal by December 2023 following junta request
- UNIFIL (Lebanon): Under increasing pressure amid Israel-Hezbollah tensions
Challenges and Reforms:
- Adapting to increasingly non-permissive operating environments
- Budget constraints affecting operational capabilities
- Calls for more robust protection of civilian mandates
- Implementation of Action for Peacekeeping (A4P) initiative to improve effectiveness
International Court Mechanisms
Multiple international legal mechanisms address conflict-related violations and accountability.
International Court of Justice (ICJ)
- South Africa’s case against Israel regarding Gaza operations
- Ukraine v. Russia proceedings regarding application of Genocide Convention
- Multiple pending cases regarding territorial disputes with conflict potential
International Criminal Court (ICC)
- Ongoing investigation into situation in Ukraine including deportation of children
- Investigation into alleged war crimes in Palestinian territories
- Arrest warrant for Russian President Putin on allegations of unlawful deportation of children
Special Tribunals and Hybrid Courts
- UN Investigative Team for Accountability of Da’esh/ISIL (UNITAD) continues evidence gathering
- Proposals for special tribunal for crime of aggression regarding Ukraine
- Discussions of accountability mechanisms for various conflict situations
Regional Organizations and Mediation Efforts
Regional bodies play crucial roles in conflict prevention and resolution within their spheres.
African Union (AU)
- High-Level Panel on Sudan seeking to coordinate peace efforts
- Implementation monitoring of Ethiopia peace agreement
- Transitioning security responsibilities in Somalia
- Mediation in various electoral and constitutional disputes
European Union (EU)
- Facilitating Belgrade-Pristina dialogue on Kosovo normalization
- Supporting Ukraine through comprehensive assistance package
- Mediterranean naval operations addressing migration and arms trafficking
- Sanctions regimes targeting conflict actors in multiple contexts
ASEAN
- Limited progress on Myanmar crisis through Special Envoy mechanism
- Conflict prevention initiatives in South China Sea disputes
- Humanitarian coordination for regional crises
Emerging Trends in International Conflict
Technology and Warfare Evolution
Modern conflicts increasingly feature technological elements transforming traditional warfare.
Drone Warfare Proliferation
- Commercial drone adaptation for military purposes accelerating
- Counter-drone technologies rapidly evolving
- Autonomous capabilities raising ethical and legal questions
- Lowered barriers to entry for non-state actors
Cyber Dimensions of Conflict
- Critical infrastructure increasingly targeted during physical conflicts
- Information operations integrated with conventional warfare
- Attribution challenges complicating deterrence and response
- Expanding gray zone operations below threshold of armed conflict
Space Domain Contestation
- Anti-satellite capabilities demonstrated by multiple nations
- Communications and GPS infrastructure vulnerable during conflicts
- Space-based intelligence capabilities transforming battlefield awareness
- Emerging norms and legal frameworks struggling to keep pace with technology
Climate-Conflict Nexus
Climate change increasingly functions as a threat multiplier in conflict situations.
Resource Competition
- Water scarcity driving tensions in multiple river basins
- Changing agricultural viability forcing population movements
- Fishing ground disputes intensifying with changing marine ecosystems
- Pastoralist-farmer conflicts exacerbated by changing environmental conditions
Displacement Dynamics
- Climate-induced migration changing demographic patterns in fragile regions
- Urban infrastructure strains from rapid population movements
- Cross-border migrations creating diplomatic tensions
- Legal frameworks for climate refugees remains underdeveloped
Adaptation and Resilience
- Climate adaptation programs increasingly integrated with peacebuilding
- Disaster response capabilities becoming security priorities
- Resource governance reforms addressing conflict triggers
- Early warning systems linking climate and conflict indicators
Privatization of Security
Non-state actors play increasingly prominent roles in conflict zones globally.
Private Military Companies
- Wagner Group’s evolving role following Prigozhin’s death
- Proliferation of PMCs across African conflict zones
- Accountability gaps in operations and human rights compliance
- Blurring lines between state and private security operations
Non-State Armed Groups
- Fragmentation of armed groups creating complex conflict ecosystems
- Terrorist organizations adapting to counter-terrorism pressure
- Criminal-political nexus in multiple conflict environments
- Technology democratization enabling smaller groups to wield outsized impact
Humanitarian Response Challenges
Access Constraints
Humanitarian organizations face increasing difficulties reaching populations in need.
Politicization of Aid
- Humanitarian access increasingly used as battlefield leverage
- Aid worker security incidents at historically high levels
- Sanctions regimes creating operational complications
- Local humanitarian actors facing pressure from conflict parties
Funding Shortfalls
- Multiple major crises competing for limited donor resources
- Long-term displacement situations facing chronic underfunding
- Development-humanitarian nexus approaches seeking sustainable solutions
- Localization agenda advancing but funding flows still predominantly international
Protection of Civilians
Civilian protection remains a central concern across conflict zones.
Urban Warfare Impacts
- Increasing proportion of conflicts fought in populated areas
- Explosive weapons in urban areas causing predictable civilian harm
- Critical infrastructure damage creating cascading humanitarian effects
- Displacement patterns increasingly urban-to-urban rather than to camps
Children in Conflict
- Education disrupted for millions in conflict zones
- Child recruitment by armed groups continuing in multiple contexts
- Psychological impacts creating long-term developmental concerns
- Family separation during displacement creating protection risks
Conclusion: Pathways Forward
The landscape of international conflict remains complex and challenging, yet certain pathways offer potential for improved outcomes:
Multilateral Engagement
Despite challenges, multilateral institutions remain essential forums for conflict resolution, particularly when major powers find areas of common interest even amid broader disagreements.
Local Peacebuilding
Increasing recognition that sustainable peace requires meaningful inclusion of local communities, women, youth, and civil society in peace processes rather than top-down impositions.
Technological Governance
Emerging efforts to establish norms, regulations, and ethical frameworks for new technologies in warfare show promise for mitigating some emerging risks.
Climate-Security Integration
Growing incorporation of climate considerations into security planning and conflict prevention represents an important evolution in addressing root causes.
As the international community navigates these complex conflicts, sustained diplomatic engagement, adequate humanitarian financing, and innovative approaches to peacebuilding remain essential to addressing both immediate crises and their underlying drivers.
Understanding Global Change: Key World Events Shaping Our Future
In today’s interconnected world, world events have a profound impact on our future, from politics to climate change and technology. World Events Shaping Our Global Future provides a thorough examination of the major global events currently influencing our world, exploring their implications for economies, societies, and the environment. Whether you’re curious about international relations, global trends, or the forces shaping tomorrow’s world, this article offers valuable insights into the critical events that are shaping our collective future. Be sure to read it and stay informed about the changes that will define our world.